Introduction
Have you ever wondered how roads remain intact under intense sunlight or survive harsh winter conditions? The secret lies in a modern material called bitumen emulsion—a safer, more sustainable, and efficient solution in road construction. At the core of this advancement is the bitumen emulsion plant, a specialized system designed to manufacture this innovative material.
Understanding Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is essentially a mixture of bitumen, water, and emulsifying agents. Unlike traditional hot-applied bitumen, this emulsion can be applied at ambient temperatures, which makes the process significantly safer and more energy-efficient. Bitumen emulsions come in two main types based on the charge of the emulsifying agents—cationic and anionic. Cationic emulsions, with a positive charge, are more commonly used due to their superior adhesion with negatively charged aggregates. Anionic emulsions, on the other hand, are preferred for specific mix designs.
Bitumen emulsions are also classified based on their setting time: rapid setting (RS) emulsions are ideal for surface dressing; medium setting (MS) emulsions are typically used for premix applications and patchwork; and slow setting (SS) emulsions are best suited for prime coats and fog seals. Each grade is engineered to meet specific needs in road construction and maintenance.
What is a Bitumen Emulsion Plant?
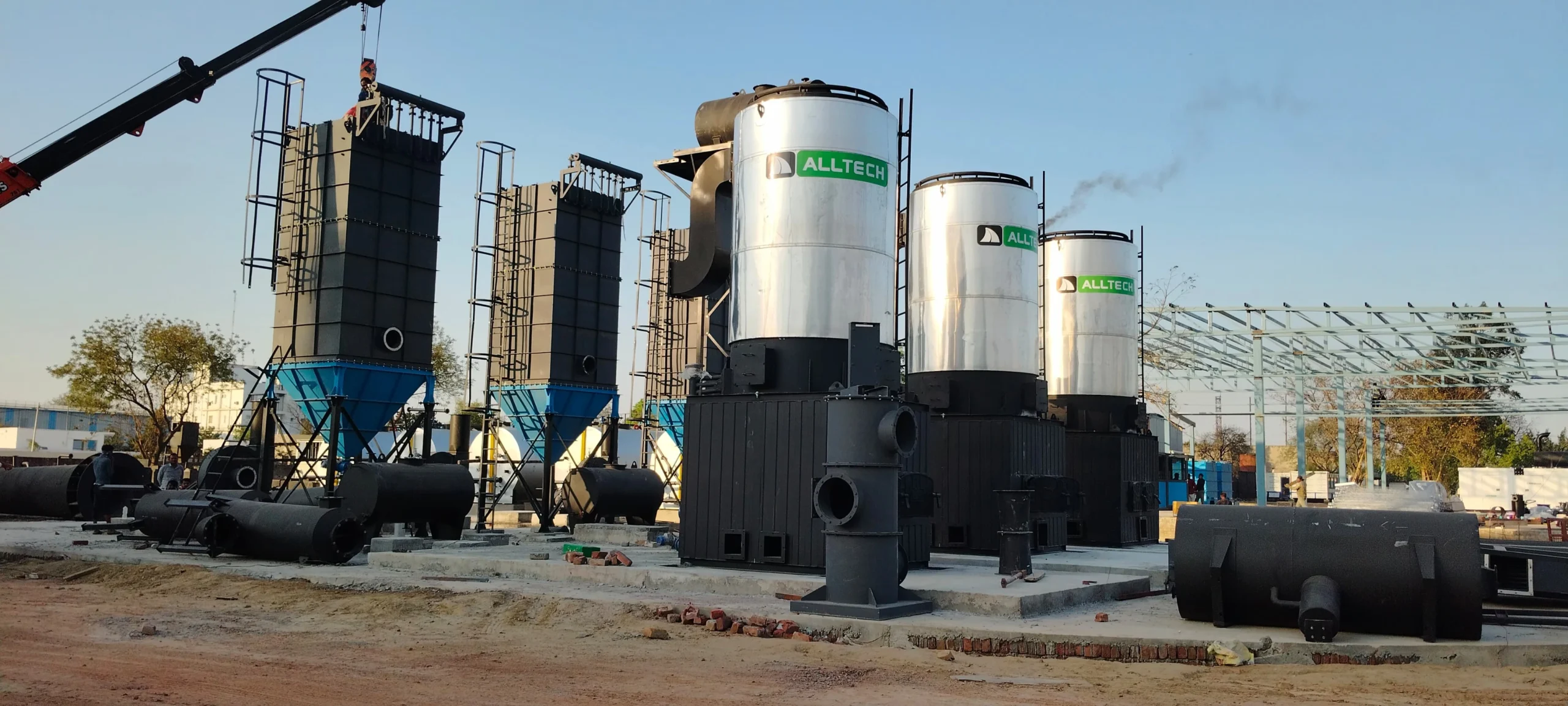
A bitumen emulsion plant is an advanced facility that produces bitumen emulsions by blending heated bitumen with water and emulsifiers under high shear conditions. The plant comprises several key components, including a colloid mill, bitumen storage tank, water tank, emulsifier dosing unit, control panel, and heat exchanger. These components work in unison to ensure consistent quality and production efficiency.
How Does It Work?
The process begins by heating the bitumen to the required temperature. Simultaneously, water and emulsifying agents are mixed in a separate preparation tank. These two streams are then introduced into the colloid mill, where high-speed mechanical agitation ensures the formation of a stable, uniform bitumen emulsion. The result is a ready-to-use material that can be applied directly for various road applications.
Types of Bitumen Emulsion Plants
Bitumen emulsion plants are available in two configurations—batch type and continuous type. Batch type plants are suitable for smaller volumes or when the production is based on specific project demands. Continuous type plants, on the other hand, are designed for high-capacity, large-scale operations where uninterrupted production is essential.
Applications and Advantages
Bitumen emulsion is widely used for surface dressing, tack coating before asphalt paving, and in cold mix applications, especially in rural or low-traffic roads. Its ability to be applied without heating enhances safety for workers and contributes to lower energy consumption. Moreover, it supports cold applications, reduces environmental impact, and allows for quicker project completion. These advantages make it a preferred choice for sustainable road infrastructure.
Comparing Bitumen Emulsion and Hot Bitumen
Compared to traditional hot bitumen, bitumen emulsion does not require high-temperature heating, making it significantly safer to handle. It reduces the risk of burns, requires less energy, and simplifies on-site application without the need for heating equipment.
Challenges in Production and Quality Control
Despite its benefits, producing high-quality bitumen emulsion requires precise control. Maintaining appropriate viscosity, achieving emulsion stability, and managing breaking time during application are some of the key challenges. To ensure consistent performance, it is essential to monitor pH levels, match viscosity to the intended application, and perform regular tests on emulsion stability and shelf life.
Maintenance of the Emulsion Plant
Proper maintenance of a bitumen emulsion plant is vital for its longevity and consistent output. Routine tasks include cleaning the colloid mill, lubricating moving parts, calibrating the dosing system, and replacing filters according to the maintenance schedule. These practices help avoid downtime and preserve plant efficiency over the long term.
Who Uses Bitumen Emulsion Plants?
Bitumen emulsion technology is widely adopted by national highway authorities, municipal development agencies, toll road operators, and private infrastructure companies. Its flexibility and eco-friendliness make it a strategic investment for both public and private sector infrastructure developers.
Setting Up a Plant
Establishing a bitumen emulsion plant requires thoughtful planning. A minimum area of 1000 square meters is typically needed, along with reliable access to power and water. Skilled operators are essential to ensure quality production. Investment considerations include the cost of plant and machinery, civil infrastructure, installation, and obtaining the necessary licenses and regulatory compliance.
The Future of Bitumen Emulsion Technology
Looking ahead, the future of bitumen emulsion is bright. Emerging innovations such as nano-additives are being explored to enhance adhesion properties. Bio-based emulsifiers are under development to make road construction even more environmentally friendly. Additionally, plant automation is expected to improve precision and efficiency, making the production process smarter and more sustainable.
Conclusion
A bitumen emulsion plant is much more than just a production unit—it represents a shift towards safer, smarter, and more sustainable road construction practices. For government bodies and private developers alike, investing in this technology is a step forward in building long-lasting, eco-friendly infrastructure that meets the needs of today and tomorrow.